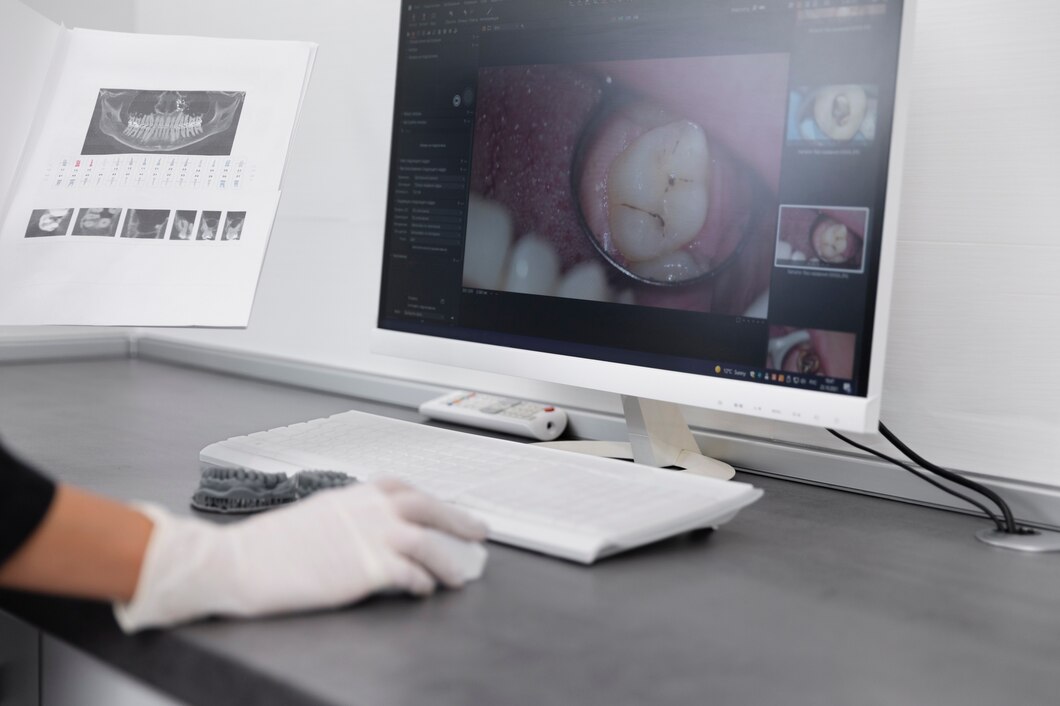
In recent years, the field of dentistry has undergone significant changes thanks to advancements in digital technology. Digital dentistry refers to the use of computer-based technology in various aspects of dental care, from diagnosis to more precise treatments. This transformation not only makes procedures more efficient but also provides a more comfortable experience and more accurate results for patients.
Intraoral Scanners
One of the main innovations in digital dentistry is the intraoral scanner. This technology allows dentists to capture digital impressions of a patient's teeth and mouth directly, without the need for physical molds, which are often uncomfortable. The 3D images produced by the intraoral scanner provide highly accurate details, allowing dentists to plan treatments with greater precision, such as orthodontic appliances, dental implants, and other aesthetic restorations.
Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAD/CAM)
Another rapidly developing technology in digital dentistry is the use of CAD/CAM (Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing)software. drg. Henytaria Fajrianti, Sp.KG, a lecturer at FKG UGM, explained that through this technology, dentists can design and produce dental restorations such as crowns, bridges, and veneers directly in the clinic. "With CAD/CAM assistance, what would normally take several days can now be completed in just one visit, saving patients time and speeding up recovery," she said.
CT Scan Technology
Additionally, digital dentistry has revolutionized the field of dental implants. With the help of digital technologies like CT scans and specialized software, dentists can plan implant placements with greater accuracy and minimize the risk of complications. Digital data allows dentists to view the bone structure in detail, ensuring that implants are placed according to the patient’s anatomical condition. This results in safer and more successful treatments.
Dental Clinic Operations
Digital dentistry also impacts how dental clinics operate. Digital management systems simplify patient record storage, treatment scheduling, and communication between doctors and patients. In addition to accelerating administrative processes, these digital systems also enhance diagnostic accuracy. The accuracy of treatment planning improves as all information is easily accessible and centralized.
Innovations in Dental Care
As technology advances, the future of digital dentistry is expected to become even more sophisticated. The use of artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze patient data, 3D printing for prosthetics, and augmented reality (AR) in dental training are just a few innovations that will transform the field. These developments aim to provide better care and more satisfying results for patients.
Digital dentistry not only changes the way dental care is delivered but also raises the standards in oral healthcare. By incorporating digital technology into dental practices, patients benefit from faster, more comfortable, and more efficient treatments. This innovation has paved the way for a new era in dentistry, focusing on comfort and optimal results for each individual.
Digital dentistry directly supports SDG Goal 3: Good Health and Well-being by improving the quality of dental healthcare services. Enhancements in precision, efficiency, and comfort positively impact overall public health and well-being. The use of digital technologies in dentistry, such as intraoral scanning, CAD/CAM, and AI, reflects progress in the medical industry, aligned with SDG Goal 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure, which encourages innovation and the development of healthcare infrastructure.
Furthermore, the advancement of dental education through digital technologies, such as AR in training, supports SDG Goal 4: Quality Education, aiming to improve educational quality in the medical field. Moreover, digital dentistry reduces the use of physical materials like dental molds, supporting more efficient and environmentally friendly consumption and production, in line with SDG Goal 12: Responsible Consumption and Production.
Author : Rizky B. Hendrawan | Photo: Freepik