Unilateral cleft lip and palate (CLPU) is a congenital anomaly characterized by failure of fusion of the lip and palatal tissues on one side. Following corrective surgeries such as cheiloplasty and palatoplasty, scar tissue often forms and may lead to maxillary deficiency, namely a lack of bone in the upper jaw, particularly in the smaller segment (minor segment). Orthodontic management of maxillary expansion using appliances such as the Quad Helix is one approach to improve the maxillary arch and expand the maxillary dento-palatal region. However, the success of this procedure is influenced by technical and anatomical factors, including the presence of scar tissue, tissue tension from the upper lip, and the condition of the surrounding bone.
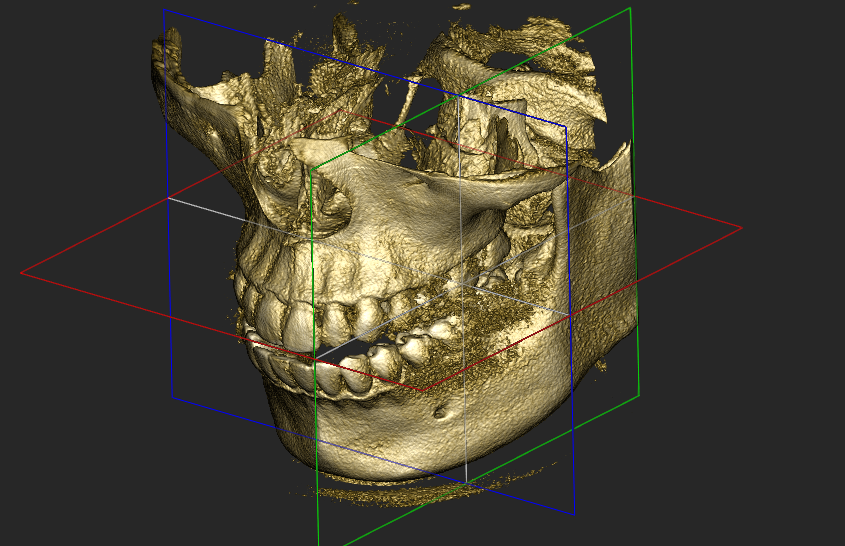
CBCT (Cone Beam Computed Tomography) has become a very important modality in three-dimensional anatomical evaluation in patients with CLPU, as it allows visualization of bony structures, the position of the major and minor maxillary segments, and provides data for simulation and planning of bone movement using orthodontic appliances.
Study References and CBCT Findings
In a study conducted by an FKG UGM student, Riona Ulfah, under the supervision of Dr. drg. Cendrawasih Andusyana Farmasyanti, M.Kes.Sp.Ort(K), and drg. Christnawati, M.Kes, Sp.Ort(K), entitled “Maxillary Movement Due to the Influence of Scar Tissue in Quad Helix Expansion Treatment in Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Cases (Finite Element Analysis)”, it was found that a 3D maxillary model was obtained from CBCT scans of CLPU patients and combined with a Quad Helix appliance model for FEA simulation. The 3D maxillary model derived from CBCT scans of CLPU patients and the 3D Quad Helix model were developed and simulated using FEA software. The first simulation was performed by applying Quad Helix expansion forces. The second simulation applied Quad Helix expansion along with scar tissue and upper lip tension. Maxillary movement was observed in the transverse, vertical, and sagittal directions. The study results showed that when expansion was applied, the major and minor segments moved differently: the major segment exhibited smaller movements in the transverse and sagittal directions compared to the minor segment, especially when forces from scar tissue and the upper lip were also taken into account.
Clinical Implications in CLPU Management
Based on these findings and the potential of CBCT, the following clinical implications can be highlighted:
- Pre-Orthodontic Planning and Simulation
CBCT scanning provides accurate 3D anatomical data to create digital maxillary models, including major and minor segments, scar tissue, and their relationship to the upper lip. Expansion force simulations allow prediction of expected bone movement and potential obstacles, such as scar tissue tension. - Identification of Obstruction Sites and Intervention Strategies
As scar tissue in the anterior region of the minor segment was found to be the greatest barrier to maxillary movement, CBCT helps identify these locations so that additional interventions (for example, scar tissue release or modification of the Quad Helix design) can be performed. - Monitoring of Bone and Anatomical Changes
With CBCT, bone movement in the transverse, sagittal, and vertical directions can be monitored periodically, and the effects of orthodontic appliances can be evaluated against actual changes in bone tissue and facial structures. - Reducing the Risk of Side Effects
CBCT enables evaluation of sensitive aspects such as root proximity, changes in maxillary shape, and effects on the sinus surfaces or nasal cavity, thereby minimizing the risk of tissue damage or complications.
***
CBCT plays an important role in the evaluation and management of CLPU (unilateral cleft lip and palate), particularly in maxillary expansion treatment using the Quad Helix. With 3D data from CBCT, finite element simulations can demonstrate how scar tissue and upper lip tension influence maxillary movement in the minor and major segments. This allows for more thorough clinical planning, targeted interventions, and better aesthetic and functional outcomes for patients. The use of CBCT is supported by scientific evidence and is relevant to the principles of health and sustainable innovation.
References
RIONA ULFAH, Dr. Dr. drg. Cendrawasih Andusyana Farmasyanti, M.Kes.Sp.Ort(K), drg. Christnawati, M.Kes, Sp.Ort(K), Maxillary Movement Due to the Influence of Scar Tissue in Quad Helix Expansion Treatment in Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Cases (Finite Element Analysis), https://etd.repository.ugm.ac.id/penelitian/detail/234938
Author: Rizky B. Hendrawan | Photo: Freepik